Timer Interrupt-Driven Multi-Task Management
How to manage multiple tasks in a timer interrupt-driven way
Background
In bare-metal programming on MicroBlaze, it’s common to need to run multiple tasks with different execution intervals. An RTOS is often a good choice, but for simple tasks an RTOS can be heavy. Another viable option is timer-interrupt-driven task scheduling.
Below is a comparison between interrupt-based task scheduling (timer-driven) and RTOS-based task scheduling:
- Task scheduling method
- Timer-based multi-tasking with multiple priorities: tasks are typically triggered by timer interrupts and switched using time-slicing or priority decisions. Task management is usually implemented with polling or interrupt-driven mechanisms. You must manage task execution order manually, and tasks typically communicate via global variables, flags, or software interrupts.
- RTOS-based multi-task scheduling: the RTOS kernel handles scheduling and provides preemptive or cooperative task scheduling. Strategies include priority scheduling, time-slicing, and preemptive scheduling. Tasks can synchronize and communicate using semaphores, message queues, and event flags.
- System complexity
- Timer-based: simple code logic, suitable for simple embedded systems without complex task management. Task switching depends on periodic timer triggers and may require manual priority control. Maintenance becomes difficult as tasks increase.
- RTOS-based: provides full features like task management, synchronization, and memory management, suitable for complex real-time systems. Easier to scale and supports dynamic task management and flexible priority control. Requires learning RTOS APIs and concepts and consumes more system resources.
- Real-time guarantees
- Timer-based: real-time behavior depends on timer and interrupt handling efficiency. If a task runs too long it may affect others. Scheduling is usually fixed and cannot dynamically adjust priorities. Suitable for low real-time-requirement scenarios like simple sensor sampling or LED control.
- RTOS-based: priority scheduling and preemption ensure high-priority tasks run promptly. Suitable for strict timing requirements such as industrial control, automotive electronics, and medical devices.
- Scalability
- Timer-based: poor scalability. As the number of tasks grows, managing timers and scheduling becomes much more complex. Manual management of task triggers and execution makes it hard to adapt to dynamic requirements.
- RTOS-based: good scalability. Supports dynamic creation and deletion of tasks, using queues and semaphores for efficient inter-task communication, suitable for multi-tasking systems with complex logic.
| Applicable scenario | Design approach |
|---|---|
| Timer-based | Simple embedded systems with few, fixed tasks, e.g., LED control, periodic sensor sampling. |
| RTOS-based | Complex embedded systems requiring multi-task scheduling and real-time guarantees, e.g., robot control, industrial automation. |
Summary
- Timer-based scheduling fits systems with few tasks and low real-time requirements: simple logic but hard to extend.
- RTOS-based scheduling fits systems with many tasks and high real-time requirements: flexible scheduling but higher resource consumption. Choose timer-based scheduling for simple, resource-constrained systems; choose an RTOS when you need better real-time behavior and scalability.
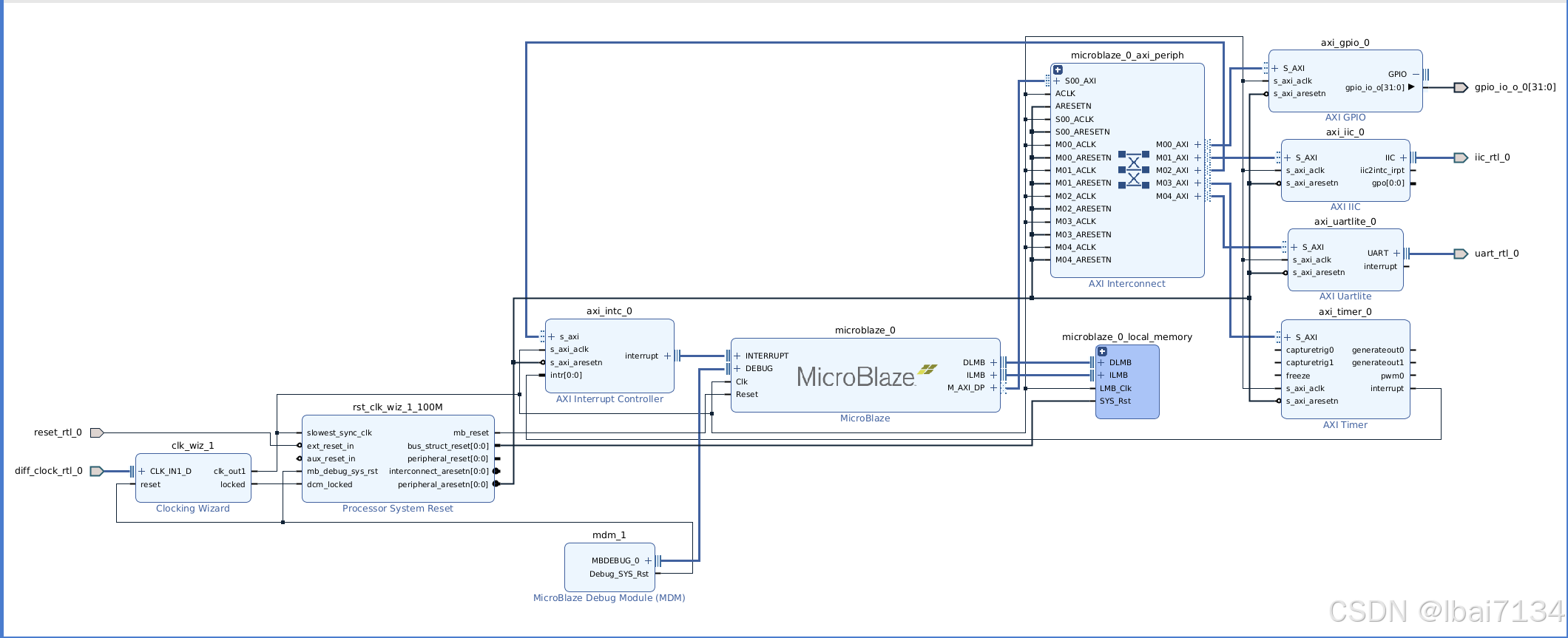
Hardware design
Required peripherals: Timer and GPIO. Optional peripherals like I²C and UART can be omitted.
The corresponding block design TCL code is as follows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
391
392
393
394
395
396
397
398
399
400
401
402
403
404
405
406
407
# ...existing code...
################################################################
# This is a generated script based on design: design_1
#
# Though there are limitations about the generated script,
# the main purpose of this utility is to make learning
# IP Integrator Tcl commands easier.
################################################################
namespace eval _tcl {
proc get_script_folder {} {
set script_path [file normalize [info script]]
set script_folder [file dirname $script_path]
return $script_folder
}
}
variable script_folder
set script_folder [_tcl::get_script_folder]
################################################################
# Check if script is running in correct Vivado version.
################################################################
set scripts_vivado_version 2023.2
set current_vivado_version [version -short]
if { [string first $scripts_vivado_version $current_vivado_version] == -1 } {
puts ""
if { [string compare $scripts_vivado_version $current_vivado_version] > 0 } {
catch {common::send_gid_msg -ssname BD::TCL -id 2042 -severity "ERROR" " This script was generated using Vivado <$scripts_vivado_version> and is being run in <$current_vivado_version> of Vivado. Sourcing the script failed since it was created with a future version of Vivado."}
} else {
catch {common::send_gid_msg -ssname BD::TCL -id 2041 -severity "ERROR" "This script was generated using Vivado <$scripts_vivado_version> and is being run in <$current_vivado_version> of Vivado. Please run the script in Vivado <$scripts_vivado_version> then open the design in Vivado <$current_vivado_version>. Upgrade the design by running \"Tools => Report => Report IP Status...\", then run write_bd_tcl to create an updated script."}
}
return 1
}
################################################################
# START
################################################################
# To test this script, run the following commands from Vivado Tcl console:
# source design_1_script.tcl
# If there is no project opened, this script will create a
# project, but make sure you do not have an existing project
# <./myproj/project_1.xpr> in the current working folder.
set list_projs [get_projects -quiet]
if { $list_projs eq "" } {
create_project project_1 myproj -part xc7a12ticsg325-1L
}
# CHANGE DESIGN NAME HERE
variable design_name
set design_name design_1
# If you do not already have an existing IP Integrator design open,
# you can create a design using the following command:
# create_bd_design $design_name
# Creating design if needed
set errMsg ""
set nRet 0
set cur_design [current_bd_design -quiet]
set list_cells [get_bd_cells -quiet]
if { ${design_name} eq "" } {
# USE CASES:
# 1) Design_name not set
set errMsg "Please set the variable <design_name> to a non-empty value."
set nRet 1
} elseif { ${cur_design} ne "" && ${list_cells} eq "" } {
# USE CASES:
# 2): Current design opened AND is empty AND names same.
# 3): Current design opened AND is empty AND names diff; design_name NOT in project.
# 4): Current design opened AND is empty AND names diff; design_name exists in project.
if { $cur_design ne $design_name } {
common::send_gid_msg -ssname BD::TCL -id 2001 -severity "INFO" "Changing value of <design_name> from <$design_name> to <$cur_design> since current design is empty."
set design_name [get_property NAME $cur_design]
}
common::send_gid_msg -ssname BD::TCL -id 2002 -severity "INFO" "Constructing design in IPI design <$cur_design>..."
} elseif { ${cur_design} ne "" && $list_cells ne "" && $cur_design eq $design_name } {
# USE CASES:
# 5) Current design opened AND has components AND same names.
set errMsg "Design <$design_name> already exists in your project, please set the variable <design_name> to another value."
set nRet 1
} elseif { [get_files -quiet ${design_name}.bd] ne "" } {
# USE CASES:
# 6) Current opened design, has components, but diff names, design_name exists in project.
# 7) No opened design, design_name exists in project.
set errMsg "Design <$design_name> already exists in your project, please set the variable <design_name> to another value."
set nRet 2
} else {
# USE CASES:
# 8) No opened design, design_name not in project.
# 9) Current opened design, has components, but diff names, design_name not in project.
common::send_gid_msg -ssname BD::TCL -id 2003 -severity "INFO" "Currently there is no design <$design_name> in project, so creating one..."
create_bd_design $design_name
common::send_gid_msg -ssname BD::TCL -id 2004 -severity "INFO" "Making design <$design_name> as current_bd_design."
current_bd_design $design_name
}
common::send_gid_msg -ssname BD::TCL -id 2005 -severity "INFO" "Currently the variable <design_name> is equal to \"$design_name\"."
if { $nRet != 0 } {
catch {common::send_gid_msg -ssname BD::TCL -id 2006 -severity "ERROR" $errMsg}
return $nRet
}
set bCheckIPsPassed 1
##################################################################
# CHECK IPs
##################################################################
set bCheckIPs 1
if { $bCheckIPs == 1 } {
set list_check_ips "\
xilinx.com:ip:microblaze:11.0\
xilinx.com:ip:axi_uartlite:2.0\
xilinx.com:ip:axi_gpio:2.0\
xilinx.com:ip:axi_timer:2.0\
xilinx.com:ip:axi_iic:2.1\
xilinx.com:ip:axi_intc:4.1\
xilinx.com:ip:mdm:3.2\
xilinx.com:ip:clk_wiz:6.0\
xilinx.com:ip:proc_sys_reset:5.0\
xilinx.com:ip:lmb_v10:3.0\
xilinx.com:ip:lmb_bram_if_cntlr:4.0\
xilinx.com:ip:blk_mem_gen:8.4\
"
set list_ips_missing ""
common::send_gid_msg -ssname BD::TCL -id 2011 -severity "INFO" "Checking if the following IPs exist in the project's IP catalog: $list_check_ips ."
foreach ip_vlnv $list_check_ips {
set ip_obj [get_ipdefs -all $ip_vlnv]
if { $ip_obj eq "" } {
lappend list_ips_missing $ip_vlnv
}
}
if { $list_ips_missing ne "" } {
catch {common::send_gid_msg -ssname BD::TCL -id 2012 -severity "ERROR" "The following IPs are not found in the IP Catalog:\n $list_ips_missing\n\nResolution: Please add the repository containing the IP(s) to the project." }
set bCheckIPsPassed 0
}
}
if { $bCheckIPsPassed != 1 } {
common::send_gid_msg -ssname BD::TCL -id 2023 -severity "WARNING" "Will not continue with creation of design due to the error(s) above."
return 3
}
##################################################################
# DESIGN PROcs
##################################################################
# Hierarchical cell: microblaze_0_local_memory
proc create_hier_cell_microblaze_0_local_memory { parentCell nameHier } {
variable script_folder
if { $parentCell eq "" || $nameHier eq "" } {
catch {common::send_gid_msg -ssname BD::TCL -id 2092 -severity "ERROR" "create_hier_cell_microblaze_0_local_memory() - Empty argument(s)!"}
return
}
# Get object for parentCell
set parentObj [get_bd_cells $parentCell]
if { $parentObj == "" } {
catch {common::send_gid_msg -ssname BD::TCL -id 2090 -severity "ERROR" "Unable to find parent cell <$parentCell>!"}
return
}
# Make sure parentObj is hier blk
set parentType [get_property TYPE $parentObj]
if { $parentType ne "hier" } {
catch {common::send_gid_msg -ssname BD::TCL -id 2091 -severity "ERROR" "Parent <$parentObj> has TYPE = <$parentType>. Expected to be <hier>."}
return
}
# Save current instance; Restore later
set oldCurInst [current_bd_instance .]
# Set parent object as current
current_bd_instance $parentObj
# Create cell and set as current instance
set hier_obj [create_bd_cell -type hier $nameHier]
current_bd_instance $hier_obj
# Create interface pins
create_bd_intf_pin -mode MirroredMaster -vlnv xilinx.com:interface:lmb_rtl:1.0 DLMB
create_bd_intf_pin -mode MirroredMaster -vlnv xilinx.com:interface:lmb_rtl:1.0 ILMB
# Create pins
create_bd_pin -dir I -type clk LMB_Clk
create_bd_pin -dir I -type rst SYS_Rst
# Create instance: dlmb_v10, and set properties
set dlmb_v10 [ create_bd_cell -type ip -vlnv xilinx.com:ip:lmb_v10:3.0 dlmb_v10 ]
# Create instance: ilmb_v10, and set properties
set ilmb_v10 [ create_bd_cell -type ip -vlnv xilinx.com:ip:lmb_v10:3.0 ilmb_v10 ]
# Create instance: dlmb_bram_if_cntlr, and set properties
set dlmb_bram_if_cntlr [ create_bd_cell -type ip -vlnv xilinx.com:ip:lmb_bram_if_cntlr:4.0 dlmb_bram_if_cntlr ]
set_property CONFIG.C_ECC {0} $dlmb_bram_if_cntlr
# Create instance: ilmb_bram_if_cntlr, and set properties
set ilmb_bram_if_cntlr [ create_bd_cell -type ip -vlnv xilinx.com:ip:lmb_bram_if_cntlr:4.0 ilmb_bram_if_cntlr ]
set_property CONFIG.C_ECC {0} $ilmb_bram_if_cntlr
# Create instance: lmb_bram, and set properties
set lmb_bram [ create_bd_cell -type ip -vlnv xilinx.com:ip:blk_mem_gen:8.4 lmb_bram ]
set_property -dict [list \
CONFIG.Memory_Type {True_Dual_Port_RAM} \
CONFIG.use_bram_block {BRAM_Controller} \
] $lmb_bram
# Create interface connections
connect_bd_intf_net -intf_net microblaze_0_dlmb [get_bd_intf_pins dlmb_v10/LMB_M] [get_bd_intf_pins DLMB]
connect_bd_intf_net -intf_net microblaze_0_dlmb_bus [get_bd_intf_pins dlmb_v10/LMB_Sl_0] [get_bd_intf_pins dlmb_bram_if_cntlr/SLMB]
connect_bd_intf_net -intf_net microblaze_0_dlmb_cntlr [get_bd_intf_pins dlmb_bram_if_cntlr/BRAM_PORT] [get_bd_intf_pins lmb_bram/BRAM_PORTA]
connect_bd_intf_net -intf_net microblaze_0_ilmb [get_bd_intf_pins ilmb_v10/LMB_M] [get_bd_intf_pins ILMB]
connect_bd_intf_net -intf_net microblaze_0_ilmb_bus [get_bd_intf_pins ilmb_v10/LMB_Sl_0] [get_bd_intf_pins ilmb_bram_if_cntlr/SLMB]
connect_bd_intf_net -intf_net microblaze_0_ilmb_cntlr [get_bd_intf_pins ilmb_bram_if_cntlr/BRAM_PORT] [get_bd_intf_pins lmb_bram/BRAM_PORTB]
# Create port connections
connect_bd_net -net SYS_Rst_1 [get_bd_pins SYS_Rst] [get_bd_pins dlmb_v10/SYS_Rst] [get_bd_pins dlmb_bram_if_cntlr/LMB_Rst] [get_bd_pins ilmb_v10/SYS_Rst] [get_bd_pins ilmb_bram_if_cntlr/LMB_Rst]
connect_bd_net -net microblaze_0_Clk [get_bd_pins LMB_Clk] [get_bd_pins dlmb_v10/LMB_Clk] [get_bd_pins dlmb_bram_if_cntlr/LMB_Clk] [get_bd_pins ilmb_v10/LMB_Clk] [get_bd_pins ilmb_bram_if_cntlr/LMB_Clk]
# Restore current instance
current_bd_instance $oldCurInst
}
# Procedure to create entire design; Provide argument to make
# procedure reusable. If parentCell is "", will use root.
proc create_root_design { parentCell } {
variable script_folder
variable design_name
if { $parentCell eq "" } {
set parentCell [get_bd_cells /]
}
# Get object for parentCell
set parentObj [get_bd_cells $parentCell]
if { $parentObj == "" } {
catch {common::send_gid_msg -ssname BD::TCL -id 2090 -severity "ERROR" "Unable to find parent cell <$parentCell>!"}
return
}
# Make sure parentObj is hier blk
set parentType [get_property TYPE $parentObj]
if { $parentType ne "hier" } {
catch {common::send_gid_msg -ssname BD::TCL -id 2091 -severity "ERROR" "Parent <$parentObj> has TYPE = <$parentType>. Expected to be <hier>."}
return
}
# Save current instance; Restore later
set oldCurInst [current_bd_instance .]
# Set parent object as current
current_bd_instance $parentObj
# Create interface ports
set iic_rtl_0 [ create_bd_intf_port -mode Master -vlnv xilinx.com:interface:iic_rtl:1.0 iic_rtl_0 ]
set uart_rtl_0 [ create_bd_intf_port -mode Master -vlnv xilinx.com:interface:uart_rtl:1.0 uart_rtl_0 ]
set diff_clock_rtl_0 [ create_bd_intf_port -mode Slave -vlnv xilinx.com:interface:diff_clock_rtl:1.0 diff_clock_rtl_0 ]
set_property -dict [ list \
CONFIG.FREQ_HZ {100000000} \
] $diff_clock_rtl_0
# Create ports
set reset_rtl_0 [ create_bd_port -dir I -type rst reset_rtl_0 ]
set_property -dict [ list \
CONFIG.POLARITY {ACTIVE_LOW} \
] $reset_rtl_0
set gpio_io_o_0 [ create_bd_port -dir O -from 31 -to 0 gpio_io_o_0 ]
# Create instance: microblaze_0, and set properties
set microblaze_0 [ create_bd_cell -type ip -vlnv xilinx.com:ip:microblaze:11.0 microblaze_0 ]
set_property -dict [list \
CONFIG.C_DEBUG_ENABLED {1} \
CONFIG.C_D_AXI {1} \
CONFIG.C_D_LMB {1} \
CONFIG.C_I_LMB {1} \
] $microblaze_0
# Create instance: axi_uartlite_0, and set properties
set axi_uartlite_0 [ create_bd_cell -type ip -vlnv xilinx.com:ip:axi_uartlite:2.0 axi_uartlite_0 ]
# Create instance: axi_gpio_0, and set properties
set axi_gpio_0 [ create_bd_cell -type ip -vlnv xilinx.com:ip:axi_gpio:2.0 axi_gpio_0 ]
set_property -dict [list \
CONFIG.C_ALL_OUTPUTS {1} \
CONFIG.C_IS_DUAL {0} \
] $axi_gpio_0
# Create instance: axi_timer_0, and set properties
set axi_timer_0 [ create_bd_cell -type ip -vlnv xilinx.com:ip:axi_timer:2.0 axi_timer_0 ]
# Create instance: axi_iic_0, and set properties
set axi_iic_0 [ create_bd_cell -type ip -vlnv xilinx.com:ip:axi_iic:2.1 axi_iic_0 ]
# Create instance: axi_intc_0, and set properties
set axi_intc_0 [ create_bd_cell -type ip -vlnv xilinx.com:ip:axi_intc:4.1 axi_intc_0 ]
# Create instance: microblaze_0_local_memory
create_hier_cell_microblaze_0_local_memory [current_bd_instance .] microblaze_0_local_memory
# Create instance: mdm_1, and set properties
set mdm_1 [ create_bd_cell -type ip -vlnv xilinx.com:ip:mdm:3.2 mdm_1 ]
# Create instance: clk_wiz_1, and set properties
set clk_wiz_1 [ create_bd_cell -type ip -vlnv xilinx.com:ip:clk_wiz:6.0 clk_wiz_1 ]
set_property CONFIG.PRIM_SOURCE {Differential_clock_capable_pin} $clk_wiz_1
# Create instance: rst_clk_wiz_1_100M, and set properties
set rst_clk_wiz_1_100M [ create_bd_cell -type ip -vlnv xilinx.com:ip:proc_sys_reset:5.0 rst_clk_wiz_1_100M ]
# Create instance: microblaze_0_axi_periph, and set properties
set microblaze_0_axi_periph [ create_bd_cell -type ip -vlnv xilinx.com:ip:axi_interconnect:2.1 microblaze_0_axi_periph ]
set_property CONFIG.NUM_MI {5} $microblaze_0_axi_periph
# Create interface connections
connect_bd_intf_net -intf_net axi_iic_0_IIC [get_bd_intf_ports iic_rtl_0] [get_bd_intf_pins axi_iic_0/IIC]
connect_bd_intf_net -intf_net axi_intc_0_interrupt [get_bd_intf_pins axi_intc_0/interrupt] [get_bd_intf_pins microblaze_0/INTERRUPT]
connect_bd_intf_net -intf_net axi_uartlite_0_UART [get_bd_intf_ports uart_rtl_0] [get_bd_intf_pins axi_uartlite_0/UART]
connect_bd_intf_net -intf_net diff_clock_rtl_0_1 [get_bd_intf_ports diff_clock_rtl_0] [get_bd_intf_pins clk_wiz_1/CLK_IN1_D]
connect_bd_intf_net -intf_net microblaze_0_M_AXI_DP [get_bd_intf_pins microblaze_0/M_AXI_DP] [get_bd_intf_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/S00_AXI]
connect_bd_intf_net -intf_net microblaze_0_axi_periph_M00_AXI [get_bd_intf_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/M00_AXI] [get_bd_intf_pins axi_gpio_0/S_AXI]
connect_bd_intf_net -intf_net microblaze_0_axi_periph_M01_AXI [get_bd_intf_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/M01_AXI] [get_bd_intf_pins axi_iic_0/S_AXI]
connect_bd_intf_net -intf_net microblaze_0_axi_periph_M02_AXI [get_bd_intf_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/M02_AXI] [get_bd_intf_pins axi_intc_0/s_axi]
connect_bd_intf_net -intf_net microblaze_0_axi_periph_M03_AXI [get_bd_intf_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/M03_AXI] [get_bd_intf_pins axi_timer_0/S_AXI]
connect_bd_intf_net -intf_net microblaze_0_axi_periph_M04_AXI [get_bd_intf_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/M04_AXI] [get_bd_intf_pins axi_uartlite_0/S_AXI]
connect_bd_intf_net -intf_net microblaze_0_debug [get_bd_intf_pins mdm_1/MBDEBUG_0] [get_bd_intf_pins microblaze_0/DEBUG]
connect_bd_intf_net -intf_net microblaze_0_dlmb_1 [get_bd_intf_pins microblaze_0/DLMB] [get_bd_intf_pins microblaze_0_local_memory/DLMB]
connect_bd_intf_net -intf_net microblaze_0_ilmb_1 [get_bd_intf_pins microblaze_0/ILMB] [get_bd_intf_pins microblaze_0_local_memory/ILMB]
# Create port connections
connect_bd_net -net axi_gpio_0_gpio_io_o [get_bd_pins axi_gpio_0/gpio_io_o] [get_bd_ports gpio_io_o_0]
connect_bd_net -net axi_timer_0_interrupt [get_bd_pins axi_timer_0/interrupt] [get_bd_pins axi_intc_0/intr]
connect_bd_net -net clk_wiz_1_locked [get_bd_pins clk_wiz_1/locked] [get_bd_pins rst_clk_wiz_1_100M/dcm_locked]
connect_bd_net -net mdm_1_debug_sys_rst [get_bd_pins mdm_1/Debug_SYS_Rst] [get_bd_pins rst_clk_wiz_1_100M/mb_debug_sys_rst] [get_bd_pins clk_wiz_1/reset]
connect_bd_net -net microblaze_0_Clk [get_bd_pins clk_wiz_1/clk_out1] [get_bd_pins microblaze_0/Clk] [get_bd_pins microblaze_0_local_memory/LMB_Clk] [get_bd_pins rst_clk_wiz_1_100M/slowest_sync_clk] [get_bd_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/S00_ACLK] [get_bd_pins axi_gpio_0/s_axi_aclk] [get_bd_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/M00_ACLK] [get_bd_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/ACLK] [get_bd_pins axi_iic_0/s_axi_aclk] [get_bd_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/M01_ACLK] [get_bd_pins axi_intc_0/s_axi_aclk] [get_bd_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/M02_ACLK] [get_bd_pins axi_timer_0/s_axi_aclk] [get_bd_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/M03_ACLK] [get_bd_pins axi_uartlite_0/s_axi_aclk] [get_bd_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/M04_ACLK]
connect_bd_net -net reset_rtl_0_1 [get_bd_ports reset_rtl_0] [get_bd_pins rst_clk_wiz_1_100M/ext_reset_in]
connect_bd_net -net rst_clk_wiz_1_100M_bus_struct_reset [get_bd_pins rst_clk_wiz_1_100M/bus_struct_reset] [get_bd_pins microblaze_0_local_memory/SYS_Rst]
connect_bd_net -net rst_clk_wiz_1_100M_mb_reset [get_bd_pins rst_clk_wiz_1_100M/mb_reset] [get_bd_pins microblaze_0/Reset]
connect_bd_net -net rst_clk_wiz_1_100M_peripheral_aresetn [get_bd_pins rst_clk_wiz_1_100M/peripheral_aresetn] [get_bd_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/S00_ARESETN] [get_bd_pins axi_gpio_0/s_axi_aresetn] [get_bd_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/M00_ARESETN] [get_bd_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/ARESETN] [get_bd_pins axi_iic_0/s_axi_aresetn] [get_bd_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/M01_ARESETN] [get_bd_pins axi_intc_0/s_axi_aresetn] [get_bd_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/M02_ARESETN] [get_bd_pins axi_timer_0/s_axi_aresetn] [get_bd_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/M03_ARESETN] [get_bd_pins axi_uartlite_0/s_axi_aresetn] [get_bd_pins microblaze_0_axi_periph/M04_ARESETN]
# Create address segments
assign_bd_address -offset 0x40000000 -range 0x00010000 -target_address_space [get_bd_addr_spaces microblaze_0/Data] [get_bd_addr_segs axi_gpio_0/S_AXI/Reg] -force
assign_bd_address -offset 0x40800000 -range 0x00010000 -target_address_space [get_bd_addr_spaces microblaze_0/Data] [get_bd_addr_segs axi_iic_0/S_AXI/Reg] -force
assign_bd_address -offset 0x41200000 -range 0x00010000 -target_address_space [get_bd_addr_spaces microblaze_0/Data] [get_bd_addr_segs axi_intc_0/S_AXI/Reg] -force
assign_bd_address -offset 0x41C00000 -range 0x00010000 -target_address_space [get_bd_addr_spaces microblaze_0/Data] [get_bd_addr_segs axi_timer_0/S_AXI/Reg] -force
assign_bd_address -offset 0x40600000 -range 0x00010000 -target_address_space [get_bd_addr_spaces microblaze_0/Data] [get_bd_addr_segs axi_uartlite_0/S_AXI/Reg] -force
assign_bd_address -offset 0x00000000 -range 0x00008000 -target_address_space [get_bd_addr_spaces microblaze_0/Data] [get_bd_addr_segs microblaze_0_local_memory/dlmb_bram_if_cntlr/SLMB/Mem] -force
assign_bd_address -offset 0x00000000 -range 0x00008000 -target_address_space [get_bd_addr_spaces microblaze_0/Instruction] [get_bd_addr_segs microblaze_0_local_memory/ilmb_bram_if_cntlr/SLMB/Mem] -force
# Restore current instance
current_bd_instance $oldCurInst
validate_bd_design
save_bd_design
}
# End of create_root_design()
##################################################################
# MAIN FLOW
##################################################################
create_root_design ""
# ...existing code...
Software design
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
# ...existing code...
#include <stdio.h>
#include "xparameters.h"
#include "xintc.h"
#include "xtmrctr.h"
#include "xil_exception.h"
#include "xgpio.h"
#include "xil_printf.h"
#define LED_DEV_ID XPAR_AXI_GPIO_0_BASEADDR //LED ID
#define INTC_ID XPAR_XINTC_0_BASEADDR //Interrupt controller ID
#define TMRCTR_DEVICE_ID XPAR_XTMRCTR_0_BASEADDR //Timer device ID
#define TMRCTR_INTR_ID 0 //Timer interrupt ID
#define XIL_EXCEPTION_ID_INT 16U //Exception ID for interrupts
#define LED_Channel 1
XIntc Intc; // Interrupt controller instance
XGpio led_gpio; // LED GPIO instance
XTmrCtr Timer; // Timer instance
int TimerCount = 0; // Counter used for timing
void timer_intr_hander(void *InstancePtr);
int main() {
// print ("timer interrupt test\n");
// Initialize LED GPIO
XGpio_Initialize(&led_gpio, LED_DEV_ID);
// Set data direction for the specified GPIO channel (0 = output)
XGpio_SetDataDirection(&led_gpio, 1, 0);
// Set initial LED value
XGpio_DiscreteWrite(&led_gpio, 1, 0x0f);
// Initialize timer
XTmrCtr_Initialize(&Timer, TMRCTR_DEVICE_ID);
// Enable options for the specified timer
XTmrCtr_SetOptions(&Timer, 0, XTC_INT_MODE_OPTION | // interrupt mode
XTC_AUTO_RELOAD_OPTION | // auto-reload
XTC_DOWN_COUNT_OPTION); // down-count mode
// Set reset value for the timer
XTmrCtr_SetResetValue(&Timer, 0, 5000);
// Set timer callback: called each time timer completes a cycle
XTmrCtr_SetHandler(&Timer, timer_intr_hander, &Timer);
// Start the timer
XTmrCtr_Start(&Timer, 0);
// Initialize interrupt controller
XIntc_Initialize(&Intc, INTC_ID);
// Connect the interrupt source to its handler
XIntc_Connect(&Intc, TMRCTR_INTR_ID,
(XInterruptHandler)XTmrCtr_InterruptHandler,&Timer);
// Start the interrupt controller
XIntc_Start(&Intc, XIN_REAL_MODE);
// Enable the timer interrupt source
XIntc_Enable(&Intc, TMRCTR_INTR_ID);
// Initialize and enable exception handling
Xil_ExceptionInit();
Xil_ExceptionRegisterHandler(XIL_EXCEPTION_ID_INT,
(Xil_ExceptionHandler)XIntc_InterruptHandler,
&Intc);
Xil_ExceptionEnable();
while(1);
}
void timer_intr_hander(void *InstancePtr) { // Callback
TimerCount++; // Increment on each timer interrupt
// Task 1: run every 2 interrupts
if (TimerCount % 2 == 0) {
XGpio_DiscreteWrite(&led_gpio, 1, 0x5A);
}
// Task 2: run every 3 interrupts
if (TimerCount % 3 == 0) {
XGpio_DiscreteWrite(&led_gpio, 1, 0xA5);
}
}
# ...existing code...
Explanation of key code blocks:
- GPIO initialization and setup:
1 2 3 4 5 6
// Initialize LED GPIO XGpio_Initialize(&led_gpio, LED_DEV_ID); // Set channel direction to output XGpio_SetDataDirection(&led_gpio, 1, 0); // Set initial LED output XGpio_DiscreteWrite(&led_gpio, 1, 0x0f);
Performs 1) GPIO controller initialization; 2) sets direction to output for channel 1; 3) writes 0x0f to channel 1.
- Timer setup: ```c // Initialize timer XTmrCtr_Initialize(&Timer, TMRCTR_DEVICE_ID); // Enable timer options: interrupt, auto-reload, down-count XTmrCtr_SetOptions(&Timer, 0, XTC_INT_MODE_OPTION | XTC_AUTO_RELOAD_OPTION | XTC_DOWN_COUNT_OPTION);
// Set timer reset value XTmrCtr_SetResetValue(&Timer, 0, 5000); // Set handler called on timer completion XTmrCtr_SetHandler(&Timer, timer_intr_hander, &Timer); // Start the timer XTmrCtr_Start(&Timer, 0);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Initializes the timer in interrupt mode with auto-reload and down-count, sets the reset value to 5000 cycles, registers the callback `timer_intr_hander()`, and starts the timer.
- Interrupt handler:
```c
void timer_intr_hander(void *InstancePtr) {
TimerCount++;
if (TimerCount % 2 == 0) {
XGpio_DiscreteWrite(&led_gpio, 1, 0x5A);
}
if (TimerCount % 3 == 0) {
XGpio_DiscreteWrite(&led_gpio, 1, 0xA5);
}
}
Runs every timer interrupt. Task1 runs every 2 interrupts (writes 0x5A). Task2 runs every 3 interrupts (writes 0xA5). Every 6 interrupts both conditions occur in sequence.
- Interrupt controller setup: ```c XIntc_Initialize(&Intc, INTC_ID); XIntc_Connect(&Intc, TMRCTR_INTR_ID, (XInterruptHandler)XTmrCtr_InterruptHandler,&Timer); XIntc_Start(&Intc, XIN_REAL_MODE); XIntc_Enable(&Intc, TMRCTR_INTR_ID);
Xil_ExceptionInit(); Xil_ExceptionRegisterHandler(XIL_EXCEPTION_ID_INT, (Xil_ExceptionHandler)XIntc_InterruptHandler, &Intc); Xil_ExceptionEnable();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
Initializes the interrupt controller, connects the timer interrupt ID to the timer driver's interrupt handler, starts and enables the controller, registers the CPU exception handler, and enables exceptions.
# Simulation
The MicroBlaze testbench is very simple (generated here). No extra input signals are used — code not explained further.
```verilog
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module microblaze_tb;
// Clock and reset signals
reg clk;
reg reset;
wire clk_p;
wire clk_n;
// Differential clock generation
assign clk_p = clk;
assign clk_n = ~clk;
wire iic_rtl_0_scl_io;
wire iic_rtl_0_sda_io;
wire gpio_io_o_0;
wire uart_rtl_0_rxd;
wire uart_rtl_0_txd;
design_1_wrapper dut (
.diff_clock_rtl_0_clk_n(clk_n),
.diff_clock_rtl_0_clk_p(clk_p),
.gpio_io_o_0(gpio_io_o_0),
.iic_rtl_0_scl_io(iic_rtl_0_scl_io),
.iic_rtl_0_sda_io(iic_rtl_0_sda_io),
.reset_rtl_0(reset),
.uart_rtl_0_rxd(uart_rtl_0_rxd),
.uart_rtl_0_txd(uart_rtl_0_txd)
);
// Clock generation: 200 MHz (5 ns period)
initial begin
clk = 0;
forever #2.5 clk = ~clk;
end
// Reset generation
initial begin
reset = 0;
#100;
reset = 1;
end
// Simulation runtime
initial begin
#1000;
$stop;
end
endmodule
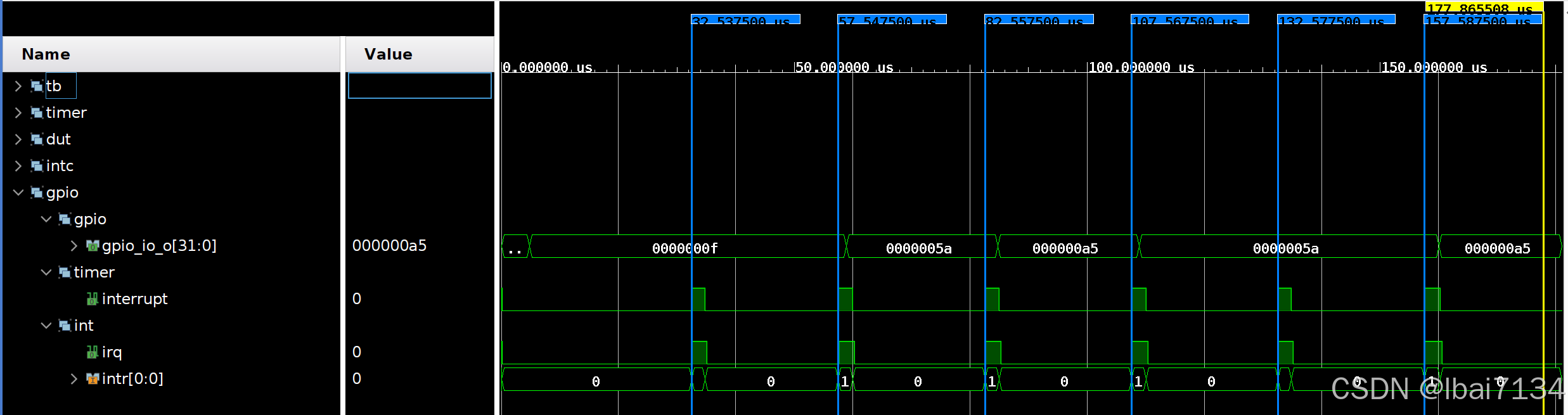
The timer generates an interrupt every 25.010000 µs, the interrupt controller asserts irq and calls the ISR to write the GPIO. Example timeline:
| GPIO | Time | TimerCount |
|---|---|---|
| 0x0f | 32.537500 µs | 1 |
| 0x5a | 57.547500 µs | 2 |
| 0xa5 | 82.557500 µs | 3 |
| 0x5a | 107.567500 µs | 4 |
| 0x5a | 132.577500 µs | 5 |
| 0xa5 | 157.587500 µs | 6 |
The interrupt interval ≈ 25.01 µs because the testbench clock is effectively 400 MHz and the clock wizard output is 200 MHz (5 ns/cycle); therefore the timer interrupt interval equals 25.01 µs / 5 ns/cycle = ~5002 cycles. This demonstrates the timer interrupt accuracy suitable for some microsecond-level applications.
Future experiments will profile and adjust Task functions to ensure they complete within the interrupt window.
References
- microblaze: AXI timer interrupt debugging — https://blog.csdn.net/YDY5659150/article/details/116236505
- MicroBlaze: UART and timer interrupt learning and test — https://blog.csdn.net/mmphhh/article/details/117373413